Zhengzhou ChangHeYue New Material CO.,LTd
Introduction
Carburizers are essential additives in metallurgy to enhance carbon content in steel and cast iron. Among them, fully graphitized and semi-graphitized carburizers dominate the market. This article explores their properties, advantages, and optimal use cases to help you make informed decisions.
1. Fully Graphitized Carburizer
Properties:
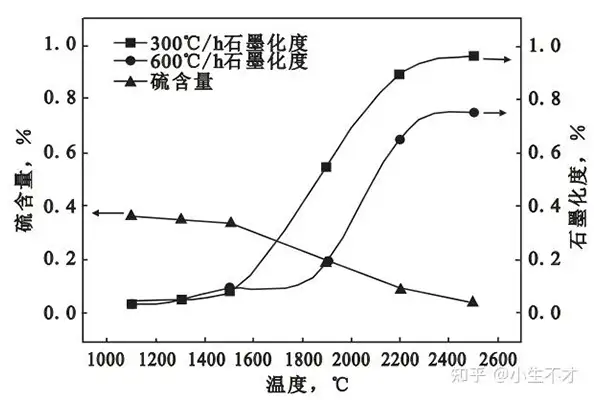
- High Crystallinity: Achieves near-perfect graphite structure (≥98% carbon).
- Low Impurities: Sulfur and nitrogen content typically below 0.05%.
- Fast Absorption: High reactivity due to ordered graphite layers, reducing dissolution time in molten metal.
Advantages:
- Superior Performance: Ideal for high-grade steel and ductile iron production, ensuring minimal slag formation.
- Consistency: Uniform carbon distribution improves mechanical properties like tensile strength.
Applications:
- Automotive components (e.g., engine blocks, gears).
- Precision casting requiring low gas porosity.
2. Semi-Graphitized Carburizer
Properties:
- Partial Crystallinity: Graphitization degree ranges 50–80%.
- Moderate Reactivity: Slower absorption than fully graphitized types but more cost-effective.
Advantages:
- Balanced Cost-Performance: Suitable for mid-range steel alloys and general foundry use.
- Flexibility: Adaptable to varying furnace conditions (e.g., induction furnaces).
Applications:
- Construction steel and machinery parts.
- Gray iron casting where extreme purity isn’t critical.
Key Comparison
| Feature | Fully Graphitized | Semi-Graphitized |
|---|---|---|
| Graphitization | ≥98% | 50–80% |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Absorption Speed | Fast | Moderate |
| Best For | High-grade alloys | General foundry work |
Conclusion
Choose fully graphitized carburizers for premium alloys requiring high purity, and semi-graphitized for cost-sensitive projects. Always verify supplier certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) for quality assurance.