Zhengzhou ChangHeYue New Material CO.,LTd
In the realm of metallurgical additives, carburizers with high sulfur content possess several distinct characteristics that can have both positive and negative implications, depending on the specific application and requirements.
1. Sulfur – Related Chemical and Physical Traits
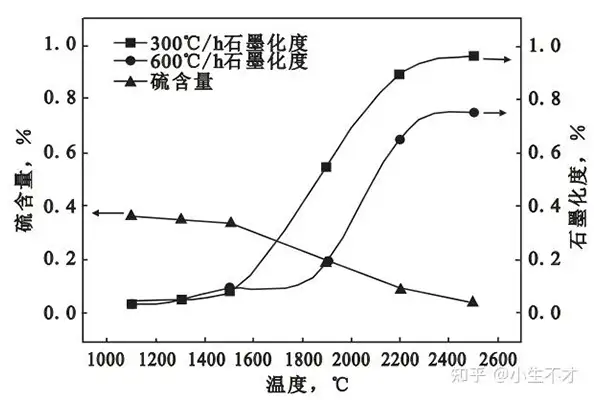
- High Sulfur Content:The most obvious characteristic of high – sulfur carburizers is, of course, their elevated sulfur levels. These carburizers typically contain a sulfur content significantly higher than the standard or low – sulfur counterparts. Sulfur exists in various chemical forms within the carburizer, often as sulfide compounds. This high sulfur presence can lead to specific chemical reactions during the melting and casting processes when added to the molten metal.
- Impact on Melting Point:Sulfur can influence the melting point of the carburizer and the overall molten metal mixture. In some cases, the presence of sulfur may slightly lower the melting point of the carburizer, which could potentially affect the melting behavior and processing temperature requirements in the furnace. However, this effect is relatively minor compared to other factors such as the carbon content and the nature of the base metal.
2. Effects on Metallurgical Processes
- Influence on Carbon Absorption:High – sulfur carburizers can have a complex impact on carbon absorption in the molten metal. In some situations, the sulfur may act as a catalyst or an aid in promoting the dissolution of carbon from the carburizer into the metal. This can potentially increase the rate of carbon absorption in the early stages of the process. However, if the sulfur content is too high, it may also cause the formation of unwanted sulfide compounds that can interfere with the carbon – metal interaction, ultimately reducing the overall carbon absorption efficiency.
- Formation of Sulfide Inclusions:One of the most notable consequences of using high – sulfur carburizers is the formation of sulfide inclusions in the final metal product. During the solidification of the molten metal, sulfur combines with certain elements, such as iron in ferrous metals, to form sulfide particles. These inclusions can have a significant impact on the microstructure and properties of the metal. Small, well – dispersed sulfide inclusions can sometimes improve the machinability of the metal, as they act as stress – raisers and help in chip formation during machining operations. However, large or clustered sulfide inclusions can be detrimental, as they can act as sites for crack initiation and propagation, reducing the mechanical properties, especially the ductility and toughness of the metal.
3. Impact on the Quality of the Final Product
- Mechanical Property Degradation:As mentioned above, the presence of sulfide inclusions from high – sulfur carburizers can lead to a degradation of the mechanical properties of the final metal product. In steel, for example, high sulfur levels can cause brittleness, especially at elevated temperatures. This is known as “hot shortness,” where the steel becomes more prone to cracking during hot – working processes such as forging and rolling. The tensile strength and impact resistance of the metal may also be negatively affected, making it less suitable for applications that require high – strength and reliable performance.
- Surface Quality Issues:High – sulfur carburizers can also cause problems related to the surface quality of the final product. Sulfur can react with the atmosphere or other elements present during the casting or heat – treatment processes, leading to the formation of surface defects such as discoloration, scaling, and porosity. These surface issues can not only affect the aesthetic appearance of the product but also its corrosion resistance and fatigue life.
4. Cost – Benefit Considerations
- Lower Cost:One of the main reasons high – sulfur carburizers may be used in some cases is their relatively lower cost compared to low – sulfur or ultra – low – sulfur carburizers. In industries where cost is a major factor and the negative impacts of sulfur can be tolerated or mitigated to some extent, high – sulfur carburizers can offer a more economical option. For example, in certain foundry applications where the final product is used in less – demanding environments or where post – processing treatments can be applied to reduce the negative effects of sulfur, the cost savings from using high – sulfur carburizers can be significant.
- Limited Applications:However, due to their negative impact on metal quality, the applications of high – sulfur carburizers are limited. They are generally not suitable for high – end manufacturing processes where strict quality control and high – performance metal products are required. Instead, they are more likely to be used in some basic foundry work or in the production of certain non – critical metal components.
In conclusion, high – sulfur carburizers have a unique set of characteristics that are a double – edged sword. While they may offer some advantages such as potential cost savings and in some cases, improved machinability, their negative impacts on metal quality, including mechanical property degradation and surface quality issues, must be carefully considered before use. Understanding these characteristics is essential for making informed decisions in metallurgical processes.