Zhengzhou ChangHeYue New Material CO.,LTd
In the field of materials and metallurgy, both fully graphitized petroleum coke and graphitized crucible scrap are important carbon – based materials, but they have distinct characteristics and differences in various aspects.
1. Raw Material and Production Origin
Fully Graphitized Petroleum Coke
- Raw Material:Fully graphitized petroleum coke is primarily derived from petroleum coke. Petroleum coke is a by – product of the oil – refining process. It is obtained after the distillation and cracking of crude oil, where heavy – oil fractions are further processed to produce coke.
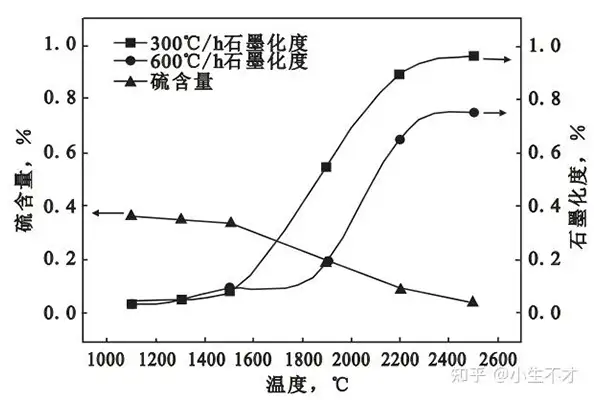
- Production Process:The production of fully graphitized petroleum coke involves a high – temperature graphitization process. Petroleum coke is heated to extremely high temperatures, typically around 2500 – 3000°C in a graphitization furnace. Under such high – temperature conditions, the structure of the petroleum coke undergoes a transformation, with the carbon atoms rearranging into a highly ordered graphite – like structure.
Graphitized Crucible Scrap
- Raw Material:Graphitized crucible scrap, as the name implies, comes from used graphitized crucibles. Graphitized crucibles are made from high – quality carbon – based raw materials, often a combination of graphite and other additives. These crucibles are used in high – temperature melting and holding operations in metallurgy, glass – making, and other industries.
- Production Process:The graphitization of crucibles is also achieved through high – temperature treatment. However, the manufacturing process of crucibles is more complex as it needs to ensure the crucible has the appropriate shape, strength, and heat – resistance properties. After the crucibles are used and discarded, they become the source of graphitized crucible scrap.
2. Physical and Chemical Properties
Fully Graphitized Petroleum Coke
- Carbon Content:Fully graphitized petroleum coke usually has a very high carbon content, often reaching over 98% or even higher. This high carbon purity makes it an excellent source of carbon for applications such as in the production of high – quality steel, where precise carbon addition is crucial.
- Crystal Structure:It has a well – developed and relatively uniform graphite – like crystal structure. The graphitization degree is high, which can be verified by techniques such as X – ray diffraction (XRD). The ordered crystal structure contributes to its good electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Particle Morphology:The particles of fully graphitized petroleum coke are often in a granular or powdered form. The particle size can be adjusted through crushing and screening processes, and it generally has a relatively regular particle – size distribution, which is beneficial for uniform mixing in various applications.
Graphitized Crucible Scrap
- Carbon Content:The carbon content of graphitized crucible scrap is also high, but it may vary depending on the original composition of the crucible. It typically contains a significant amount of carbon, but it may also have some residual impurities from the crucible – making process or substances that have interacted with the crucible during its use.
- Crystal Structure:The crystal structure of graphitized crucible scrap is also graphitic, but it may be more complex due to the presence of other additives or impurities in the original crucible material. These additives were used to enhance the crucible’s properties such as strength and thermal shock resistance, and they can affect the overall crystal structure and properties of the scrap.
- Physical Form:Graphitized crucible scrap usually comes in irregular shapes and sizes. It may be in the form of broken pieces, chunks, or a mixture of different – sized fragments, which can make it more challenging to handle and uniformly disperse in some applications compared to the more regular – shaped fully graphitized petroleum coke particles.
3. Applications
Fully Graphitized Petroleum Coke
- Steelmaking:It is widely used in the steel – making industry as a carburizer. Its high – purity carbon and good carbon – absorption characteristics make it ideal for adjusting the carbon content in molten steel, thereby improving the mechanical properties of the steel such as strength, hardness, and wear – resistance.
- Electrode Production:Fully graphitized petroleum coke is also a key raw material for the production of graphite electrodes. These electrodes are used in electric – arc furnaces for melting metals. The high electrical conductivity and thermal stability of the graphitized petroleum coke – based electrodes are crucial for efficient melting operations.
Graphitized Crucible Scrap
- Foundry and Melting Applications:Graphitized crucible scrap can be recycled and reused in foundries. It can be added to the molten metal during the casting process to provide carbon and other beneficial elements. However, due to its irregular form and possible impurity content, its use may require more careful handling and pre – treatment compared to fully graphitized petroleum coke.
- As a Component in Refractory Materials:In some cases, graphitized crucible scrap can be used as a component in the production of refractory materials. Its graphitic nature can contribute to the refractory’s heat – resistance and thermal shock – resistance properties. But again, the presence of impurities needs to be carefully considered to ensure the quality of the final refractory product.
4. Cost and Availability
Fully Graphitized Petroleum Coke
- Cost:The cost of fully graphitized petroleum coke is relatively high due to the energy – intensive graphitization process and the need for high – quality petroleum coke as the starting material. However, its high – quality and consistent properties make it a preferred choice for applications where quality is of utmost importance.
- Availability:Its availability depends on the production capacity of the petroleum – refining industry and the graphitization facilities. In regions with a well – developed oil – refining and graphitization industry, it may be more readily available.
Graphitized Crucible Scrap
- Cost:Graphitized crucible scrap is generally less expensive than fully graphitized petroleum coke. This is because it is a recycled material, and the cost of production is mainly related to the collection, sorting, and pre – treatment processes.
- Availability:The availability of graphitized crucible scrap is more limited and depends on the amount of used crucibles generated in the relevant industries. It may not be as consistently available as fully graphitized petroleum coke, and the quality and quantity can vary significantly from one source to another.
In conclusion, fully graphitized petroleum coke and graphitized crucible scrap have distinct differences in terms of their raw material origin, physical and chemical properties, applications, and cost – availability aspects. Understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions in various industrial processes where these materials are considered for use.