Zhengzhou ChangHeYue New Material CO.,LTd
(Discover technical specifications, use cases, and selection criteria for industrial carbon additives)
In metallurgy, foundry, and industrial heating applications, carbon additives play a critical role in controlling carbon content and improving product quality. This comprehensive guide clarifies the differences between 11 common carbon additive types, including graphitized petroleum coke, calcined coal, and high-nitrogen additives, to help engineers and buyers make informed decisions.
1. Carbon Additives by Raw Material Origin
| Type | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Calcined Coal | • 90%+ C content • Low Sulfur (<0.5%) • High density (2.2-2.5 g/cm³) | Electric arc furnace steelmaking, precision castings |
| Petroleum Coke | • 98-99% C • Ultra-high resistivity (10-15 μΩ·m) • Low thermal expansion | Aluminum electrolysis anodes, protective slag for steel casting |
| Pitch Coke | • 90-95% C • Volatile matter <3% • Dense structure | Glass melting furnaces, ceramic sintering |
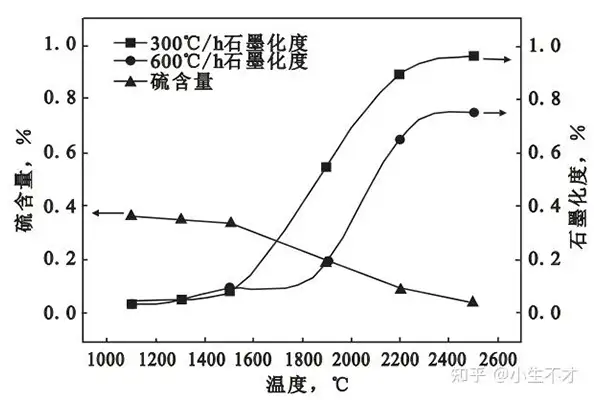
Technical Note: Calcined coal undergoes 1300°C+ calcination, while petroleum coke requires 2000°C+ graphitization for optimal performance.
2. Graphitization Degree Classification
Graphitization level directly impacts conductivity, oxidation resistance, and melting behavior:
| Grade | Graphitization Temperature | Density (g/cm³) | Electrical Resistivity (μΩ·m) | Oxidation Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Graphitized | Natural formation | 1.8-2.0 | 1,000-5,000 | Poor |
| Semi-Graphitized | 1000-1300°C | 2.0-2.3 | 500-1,000 | Moderate |
| Fully Graphitized | 1800-2200°C | 2.2-2.5 | 10-50 | Excellent |
High-Nitrogen Additive (Special Category):
- Contains 0.3-0.8% nitrogen via cyanamide carriers
- Reduces alloy element usage in IF steel production
- Carbon recovery rate: 88-91%
3. Physical Form & Processing Methods
| Form | Production Process | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode Scrap | 破碎废石墨电极 (3-15mm) | • 99%+ purity • Cost-effective | • Moisture sensitivity |
| Pelletized | Cold pressing (150-300MPa) | • Even combustion • Improved gas flow | • Higher energy cost |
| Crushed Crucible | 废坩埚回收料粉碎 (1-5mm) | • Recycled material source | • Carbon content variability |
Key Comparison:
- Columnar/Beaded Additives: Ideal for submerged arc furnaces due to low porosity and uniform thermal conductivity.
- Graphitized Electrode Scrap: Maximum oxidation resistance at 1600-1700°C for long-duration melting processes.
4. SEO-Optimized Selection Flowchart
| Process Type | Recommended Carbon Additive |
|---|---|
| Arc Furnace Steelmaking | Calcined Coal/Electrode Scrap |
| Basic Oxygen Furnace | High-Reactivity Pitch Coke |
| Non-Ferrous Melting | Low-Sulfur Petroleum Coke |
| Nitrogen Content Control | High-Nitrogen Additive |
| Cost-Sensitive Scenario | Semi-Graphitized/Crucible Crushed |
| High-Temperature Stability | Fully Graphitized Electrode Scrap |
5. Technical Parameter Benchmarking
| Additive Type | Carbon Recovery (%) | Ash Content (%) | Optimal Addition Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcined Coal | 85-90 | 7-10 | 1400-1500 |
| Graphitized Coke | 92-95 | 1.5-3 | 1600-1700 |
| High-Nitrogen Additive | 88-91 | 2-4 | 1500-1600 |
6. Future Trends in Carbon Additive Technology
- Low-Emission Solutions:
- Development of sulfur <0.1% and volatile matter <1% products for green manufacturing.
- Functional Composites:
- Calcium titanate-graphite composites for simultaneous deoxidation and desulfurization.
- Nanotechnology:
- 30-50 nm ultrafine graphite particles boosting melt penetration rate by 30%+.
Conclusion
Understanding the unique properties of carbon additives—such as graphitization level, raw material origin, and physical form—enables precise process optimization. For instance:
- Foundries requiring rapid melting should prioritize semi-graphitized pitch coke.
- Steel plants focused on low impurities must select calcined coal with <0.5% sulfur.
Download our free carbon additive comparison chart for instant access to technical specs and supplier recommendations.